This is a continuation of a series of posts on the Sony a7RIII. You should be able to find all the posts about that camera in the Category List on the right sidebar, below the Articles widget. There’s a drop-down menu there that you can use to get to all the posts in this series.
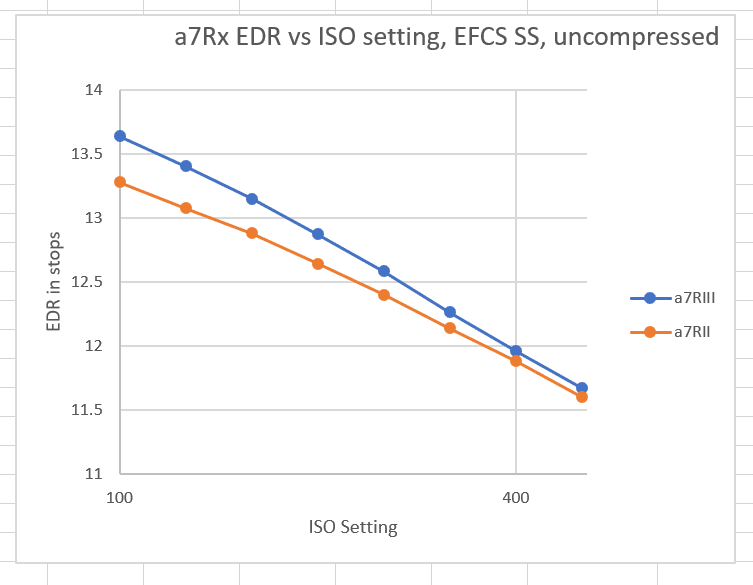
I reported here on the read noise (RN) and engineering dynamic range (EDR) of the a7RIII as the ISO control is adjusted. The a7RIII looked to be fairly ISOless at low ISO settings, more so than its predecessor. I wanted to take a look at the details. Here is the EDR of both cameras for the ISO range from 100 to 500:
You can see that the a7RIII curve is closer to the ideal straight line. The a7RII curve bends over. Bill Claff has noticed this also and speculates that the reason is that the a7RII did not actually have a 14-bit analog-to-digital converter (ADC). He thinks the camera got to 14-bit precision by making 4 12-bit conversions and summing the results. It looks like the a7RIII actually has a 14-bit ADC. It could be that there’s another source of additional post-amplification read noise in the a7RII, but I’m thinking that bill is probably right. I have a test that I can run that should shine some light on this issue, but it’s pretty involved and it’ll be a while before I get to it.
Great Jim, I am wondering, if the a7rIII really “have” 14bit, or still “supposed 14bit-compressed”?!.
It seams, it does, yet. So, I can order it now. Thanks a lot Jim.
Uncompressed raw appears to be actually 14-bit precision if we ignore the digital scaling.