This is one in a series of posts on the Nikon Z9. You should be able to find all the posts about that camera in the Category List on the right sidebar, below the Articles widget. There’s a drop-down menu there that you can use to get to all the posts in this series; just look for “Z9”.
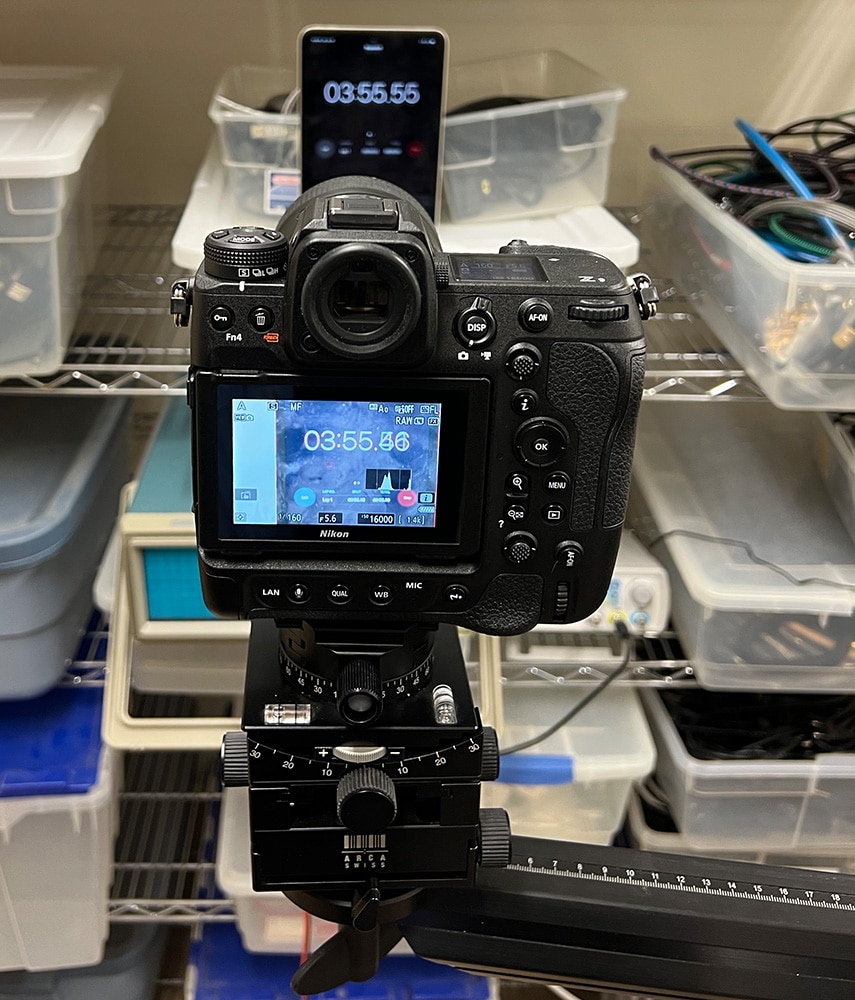
I’ve measured finder latency before by aiming the camera at a digital stopwatch and photographing both the LCD on the back of the camera and the stopwatch at the same time. I decided to try that with the Z9. A few caveats:
- The stopwatch I used has 1/100 second precision, and doesn’t always increment by 1/100 second.
- In this test, I measured static latency, not the latency when you are making a continuous series of images.
- I used a Sony a9 with mechanical shutter set to 1/800 second, and operated the camera in portrait orientation so the shutter would sweep by the stopwatch and the LCD image of the stopwatch at the same time.
- I couldn’t do this test with the EVF. The times for the EVF might be different.
- The test was performed with the digits in the upper middle of the Z9 frame. When I’ve tested other cameras, I’ve found differences in latency across the frame.
Here’s the setup:
I made about 30 images, throwing out the ones showing two digits at the same time.
The average latency shown in the remaining 22 images was 49 milliseconds. When I measured the SOny a9 using somewhat different methods, I got 35 milliseconds. I got about 25 milliseconds with the Z7 with the magnification turned off using a similar setup to what you see above.
I was unsatisfied with the variation I observe in the samples from the above test. I thought that the fast that the counter in the stopwatch is probably skipping codes probably cause a bias towards longer-than-accurate results.
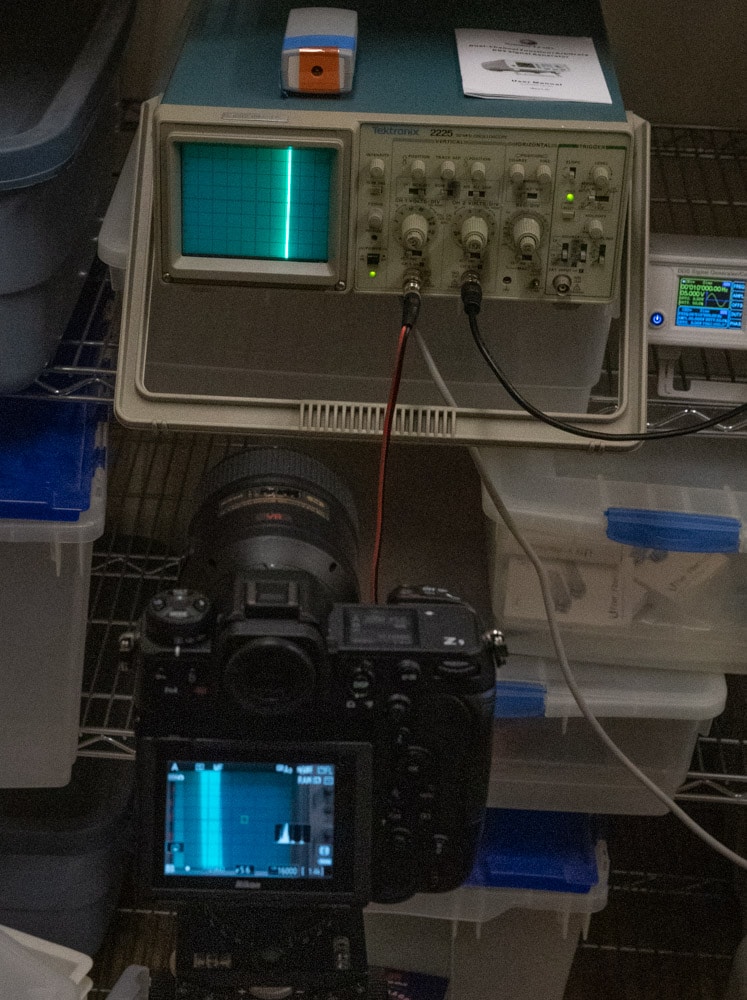
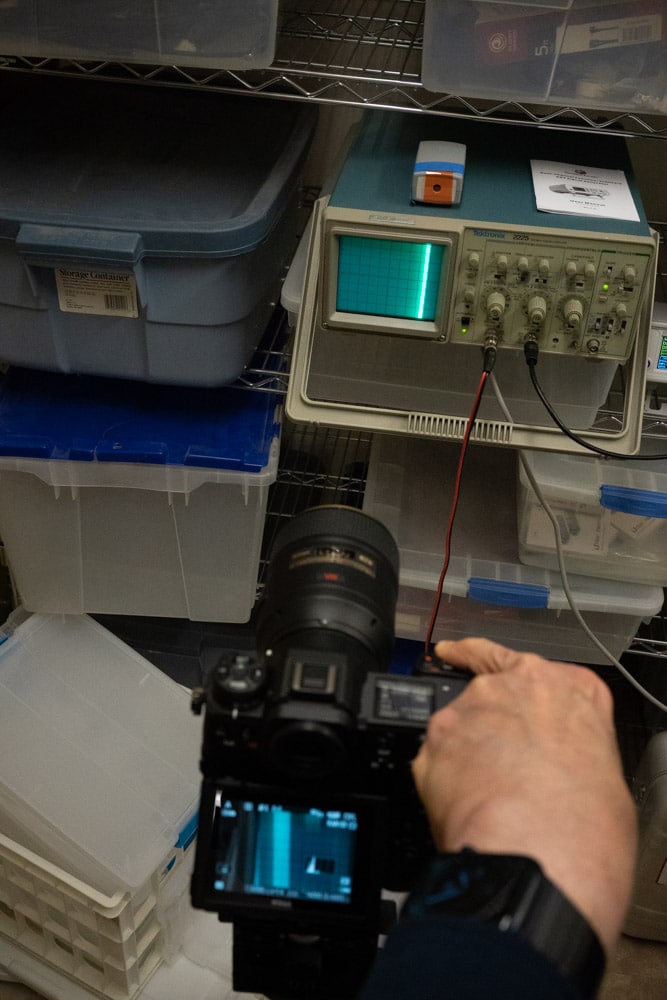
So I used an oscilloscope with a 10 KHz full scale input wave, and the time base set to 10 msec/division.
Here’s a closeup of the ‘scope:
And one of the camera:
In the dim light, I found it impossible to get both of those simultaneously in focus. The camera is making the line wider than it really is. If you use the right edge of the line, the delay is about 40 milliseconds. If you use the left edge of the line, it’s about 55 milliseconds. If you use the middle of the line, it’s about 47 or 48 milliseconds. So it looks like the stopwatch test was about right. Note that the LCD latency is lowest at the bottom of the screen, and highest at the top of the screen, with a difference of about 4 milliseconds.
When the shutter button is half-depressed, the scan rate ofthe LCD appears to double. This would have been easier if I’d three hands, but I did take some images with the camera set up that way. Since the latency dropped, I set the time ase on the scope to 5 milliseconds per division.
This is really out of focus, but I can make out the graticule lines. Looks like about 5 divisions to the right edge of the fat trace on the camera back, and 6.5 to the left edge. Call it 28 milliseconds average. The total time for the a9 shutter to traverse the frame is about 3.5 milliseconds, so it it only adding about a millisecond of uncertainty.


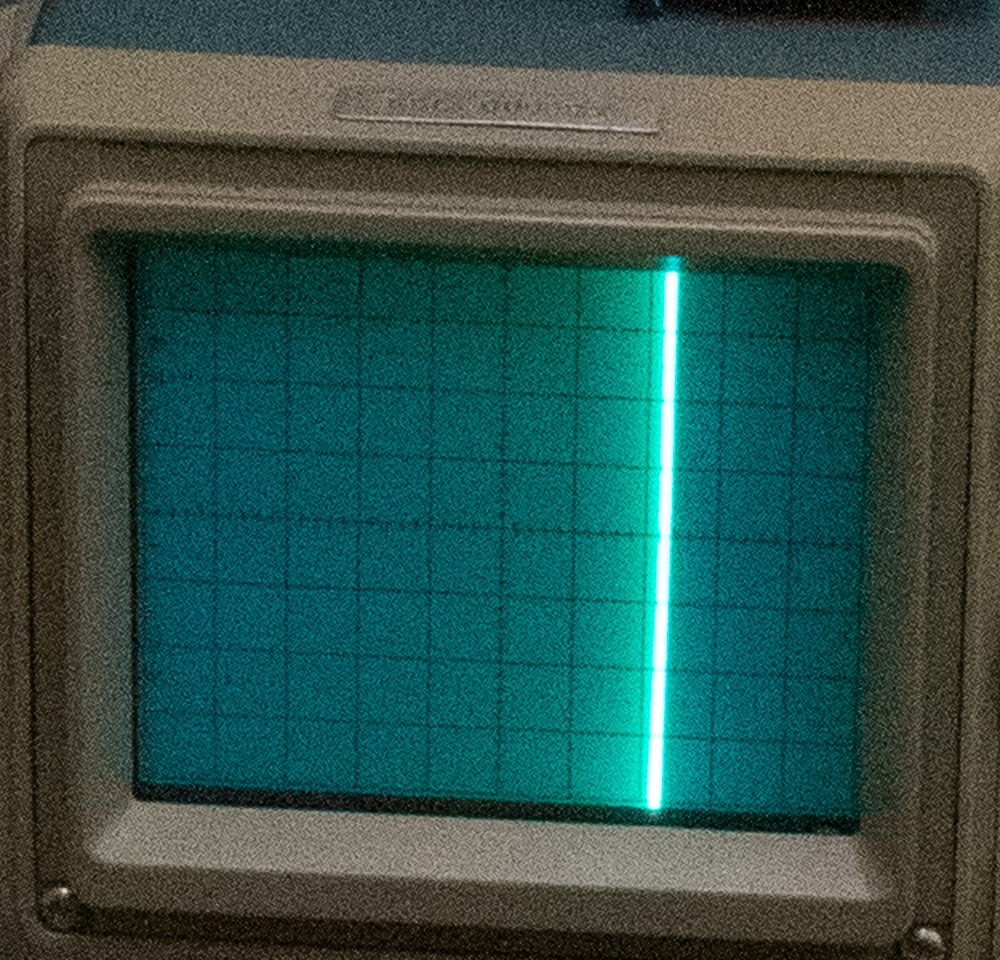


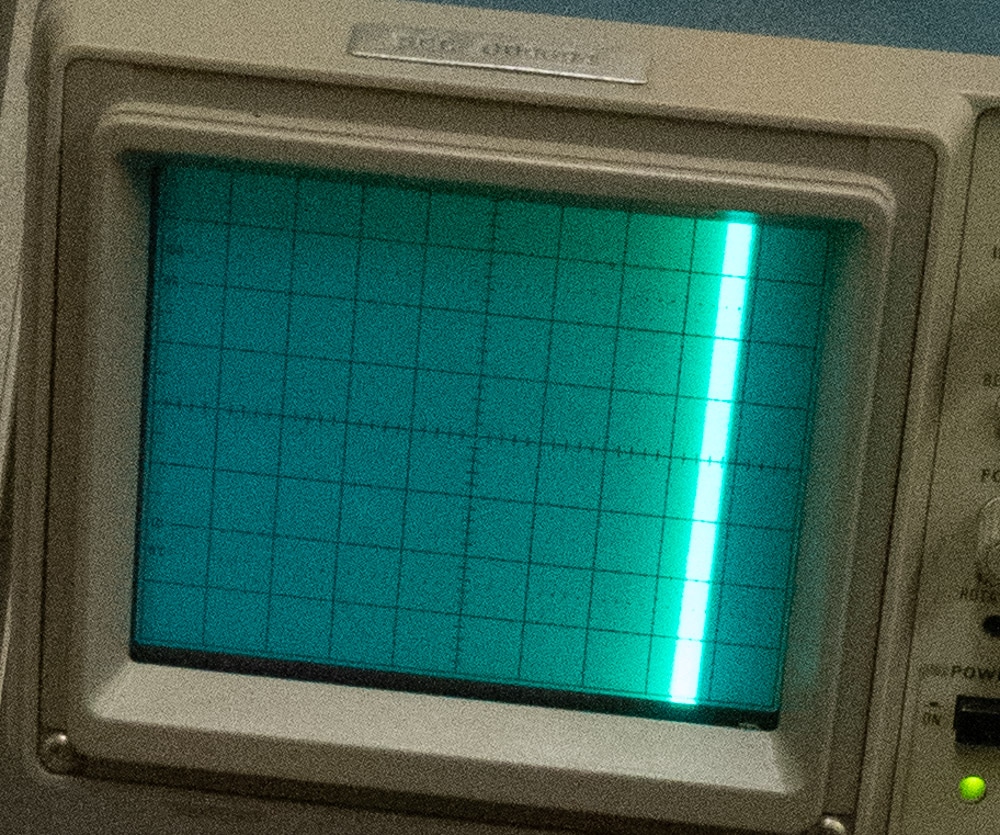

Simple solution to get focus in both displays is to use a tilted lens. This is an outstanding example of the weakness of image stacking for many purposes.
Use a mirror or two to put whatever you need in a different plane? I’m thinking on how to arrange that.
I just tried z9 in sport setting and acquiring moving subject with panning made my brain hurt. I use both eyes and the difference in timing felt off. I may have to rent z9 to see if I can deal. And think about how to mitigate. Thank you for the testing.