This is one in a series of posts on the Fujifilm GFX 100S. You should be able to find all the posts about that camera in the Category List on the right sidebar, below the Articles widget. There’s a drop-down menu there that you can use to get to all the posts in this series; just look for “GFX 100S”. Since it’s more about the lenses than the camera, I’m also tagging it with the other Fuji GFX tags.
In a previous post, I looked at the off-axis MTF50 and microcontrast of the Fuji 32-64 mm f/4 GF zoom. In this post, I’ll do the same for the 45-100 mm f/4 GF lens.
Here’s the test protocol:
- RRS carbon fiber legs
- C1 head
- 100, 150, and 200 mm focal length
- Target distance as per the table below, interpolated as required
- ISO 100
- Electronic shutter
- 10-second self timer
- f/5.6 through f/11 in whole-stop steps
- Exposure time set by camera in A mode
- Focus bracketing, step size 1, 120 to 60 exposures
- Initial focus well short of target
- Convert RAF to DNG using Adobe DNG Converter
- Extract raw mosaics with dcraw
- Extract slanted edge for each raw plane in a Matlab program that Jack Hogan originally wrote, and that I’ve been modifying for years.
- Analyze the slanted edges and produce MTF curves using MTF Mapper (great program; thanks, Frans)
- Fit curves to the MTF Mapper MTF50 values in Matlab
- Correct for systematic GFX focus bracketing inconsistencies
- Analyze and graph in Matlab
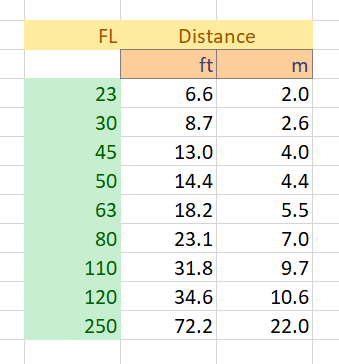
MTF50 results for the three focal lengths tested:
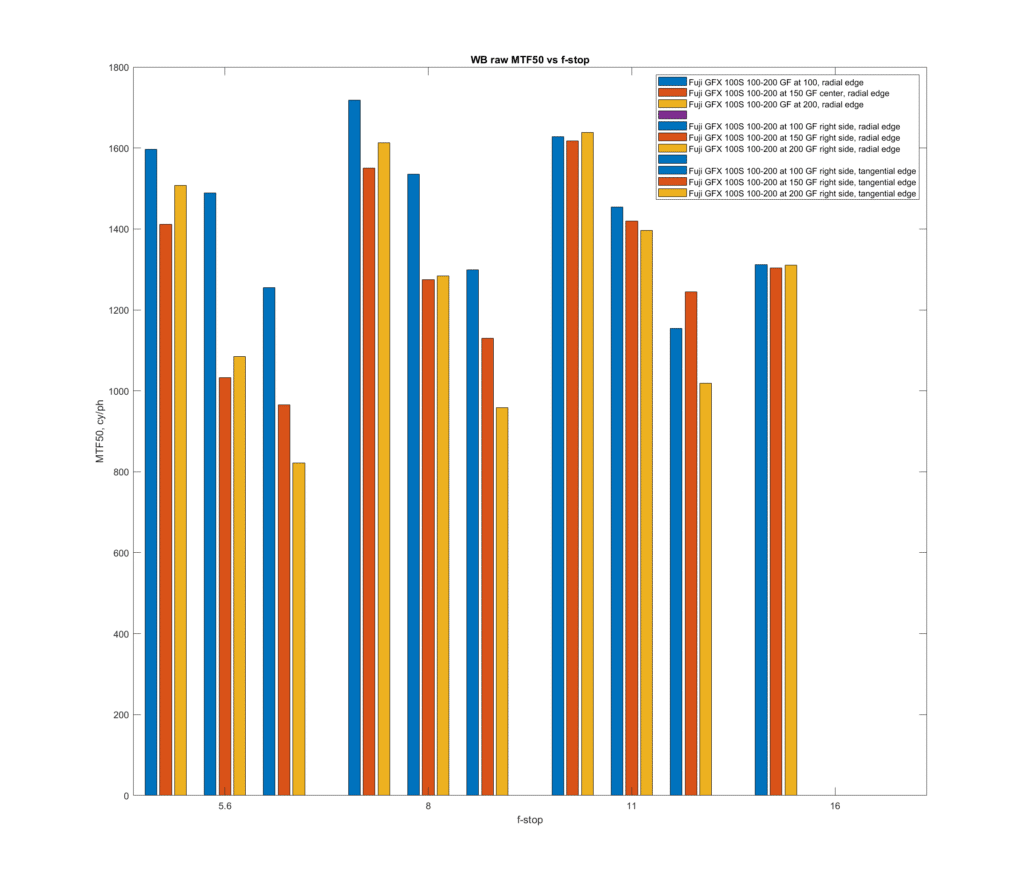
With the 110/2 thrown in for comparison:
f/8 is no longer the great equalizer. It takes f/11, and even that doesn’t do it off axis.
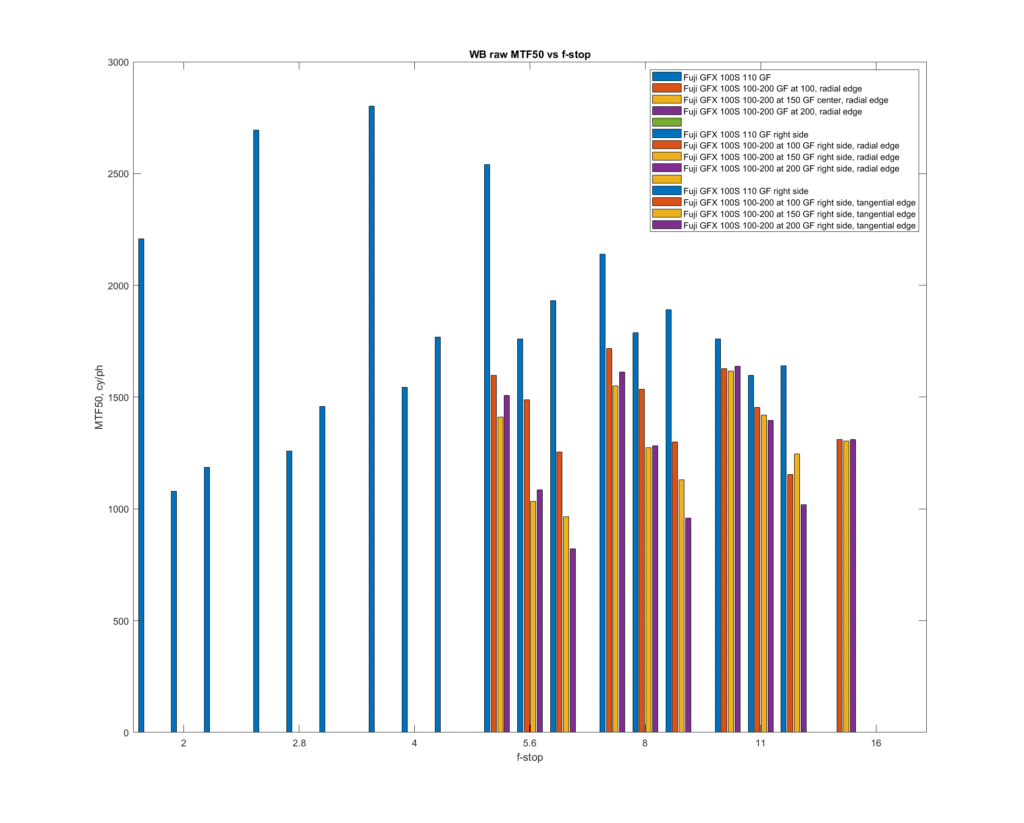
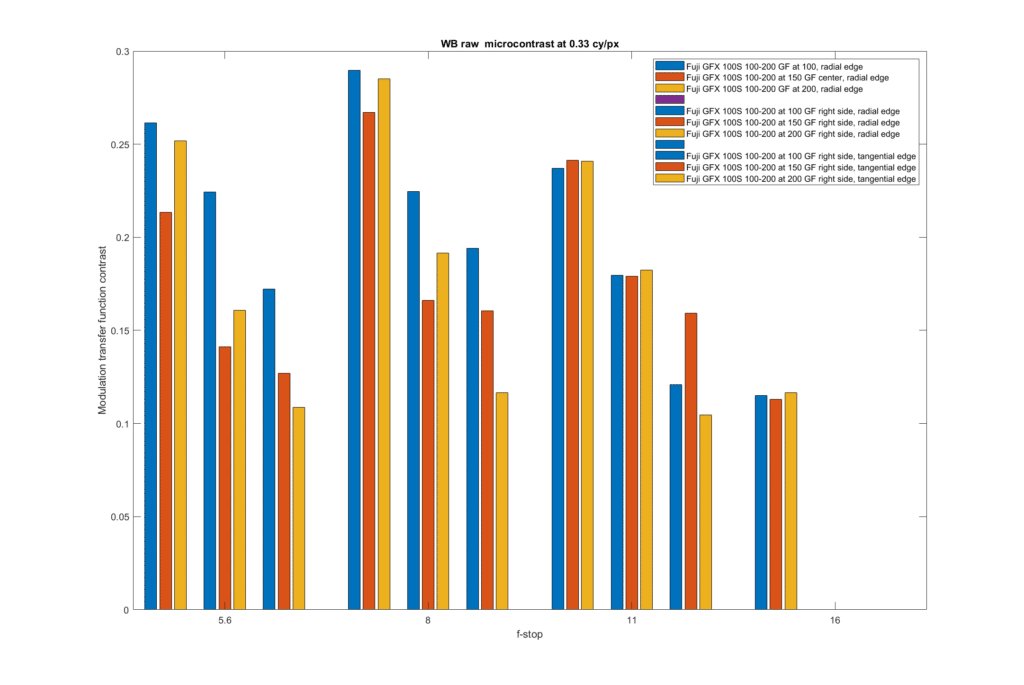
Looking at microcontrast, at 0.25 and 0.33 cycles per pixel:
Leave a Reply