In my last post, I made the assertion that, if you have a good printer, your printer can print colors you can’t represent in Adobe (1998) RGB, and therefore, you can’t see on a monitor with the Adobe RGB primaries.
I’d like to use this post to give some examples. In all the pictures to follow, I started with the profile of the printer/paper combination used for the example. I used Gamutvision to show what happens to the gamut if you convert images in that printer’s color space to Adobe RGB with relative colorimetric intent. Solid colors are successfully converted. The colors indicated by the wire-frame outlines are outside of the Adobe RGB gamut. The three dimensional graphs are in CIEL*a*b*, with the luminance axis running from bottom to top.
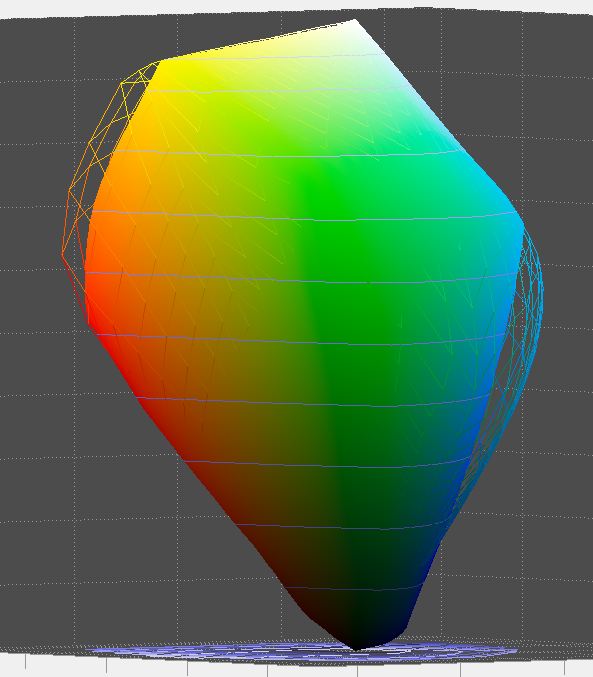
First, let’s look at Epson Premium Glossy Photo Paper on an Epson 4900. The printer profile is Epson’s.
You can see that the Adobe RGB color space can’t represent some of the medium to dark blues and cyans that the printer can print. It also has trouble with some light yellows.
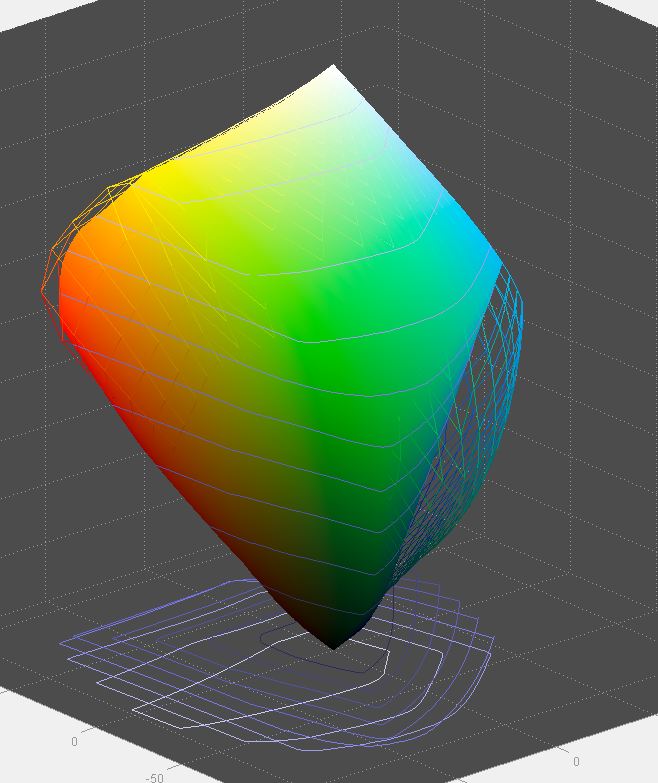
The Epson 4900 displays similar results when printing on Exhibition Fiber paper. This plot uses a profile that I made:
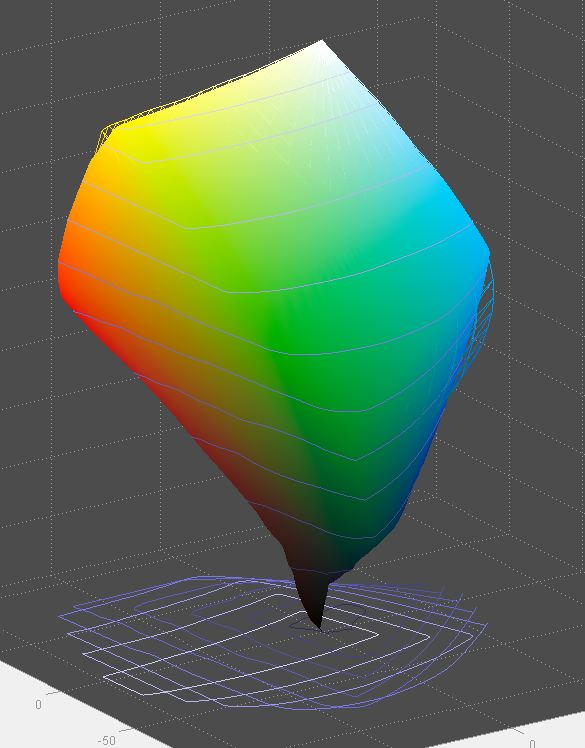
Matte papers don’t strain the Adobe displays nearly as much. Here’s what happens when you use an Epson 9800 and print on Hahnemühle Photo Rag:
There are just a few yellows, blues, and cyans that can’t be represented in Adobe RGB.
Leave a Reply